What is row echelon form?
Row echelon form is any matrix with the following properties:
All zero rows (if any) belong at the bottom of the matrix
A pivot in a non-zero row, which is the left-most non-zero value in the row, is always strictly to the right of the pivot of the row above it.
Here are a few examples of matrices in row echelon form:

![]()


Application with Gaussian Elimination
The major application of row echelon form is Gaussian elimination. In linear algebra, Gaussian elimination is a method used on coefficent matrices to solve systems of linear equations. By transforming matrices into row echelon form, the values of the variables given the coefficients becomes evident. Here is an example of transforming a matrix into row echelon form using Gaussian elimination:
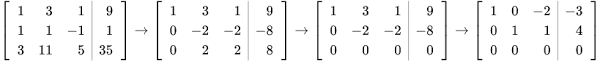
In this process, the rows are being modified by applying a series of basic operations allowed by Gaussian elimination. These details can be read about more in the definition of Gaussian elimination.
The two matrices furthest right in the image above are in row echelon form and the matrix furthest left is the original linear equations.
When matrices are transformed to row echelon form via Gaussian elimination, we can easily get properties such as:
Rank
Kernel
Inverse matrices
Solutions to linear equations
Determinants (if the matrix is square)
